Medical Science and Health Product Family
In recent years, it has been used in neurology, neurology, cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, etc. to reduce medical errors, improve the quality of clinician's education, and shorten the learning curve without risk to the patient. Simulation and simulator systems supported by mixed/virtual/augmented reality technologies, where experts will receive standard, multi-disciplinary and mixed training, have gained importance. As SimBT, we have done and are doing many R&D and Innovation projects in the field of Medical Informatics, including our teachers in our Medical Faculties, using our knowledge, experience and infrastructure from defense applications. Some of our national and global products that we have acquired as a result of these projects are explained in the following sections.

Mixed Reality Integrated Anatomy Display and Education System (ARTOMI)
The ARTOMI system helps students of health high schools, health sciences and medical faculties studying in the health sector to explore human anatomy in new and innovative ways.
ARTOMI is designed to provide a better understanding of the spatial relationships of important anatomical parts. It enables multiple people to learn interactively at the same time on an accurate, high-quality 3D virtual cadaver image that can be viewed layer by layer and piecemeal. ARTOMI; has more than 3,500 3D anatomical models of 14 systems of our body, approved by medical doctors and anatomy professors; hierarchical structures and search function based on terminologia anatomica database; all anatomical models and labels are in Turkish, English and Latin; It has exam preparation and evaluation features.
Augmented Reality Integrated Brain Surgery Surgical Training and Planning System (ArBrain)
ArBrain neurosurgeons; “increase confidence in performing delicate neurosurgical procedures”, “eliminate the need to mentally reconstruct images or project them mentally to patients”, “prevent constantly shifting vision between the surgical field and computer screen and disrupt the surgical workflow” and “in neurosurgical procedures” It is a mixed reality supported training and planning system developed to guide surgeons with high accuracy to support determining the optimal drill position and drill angle.
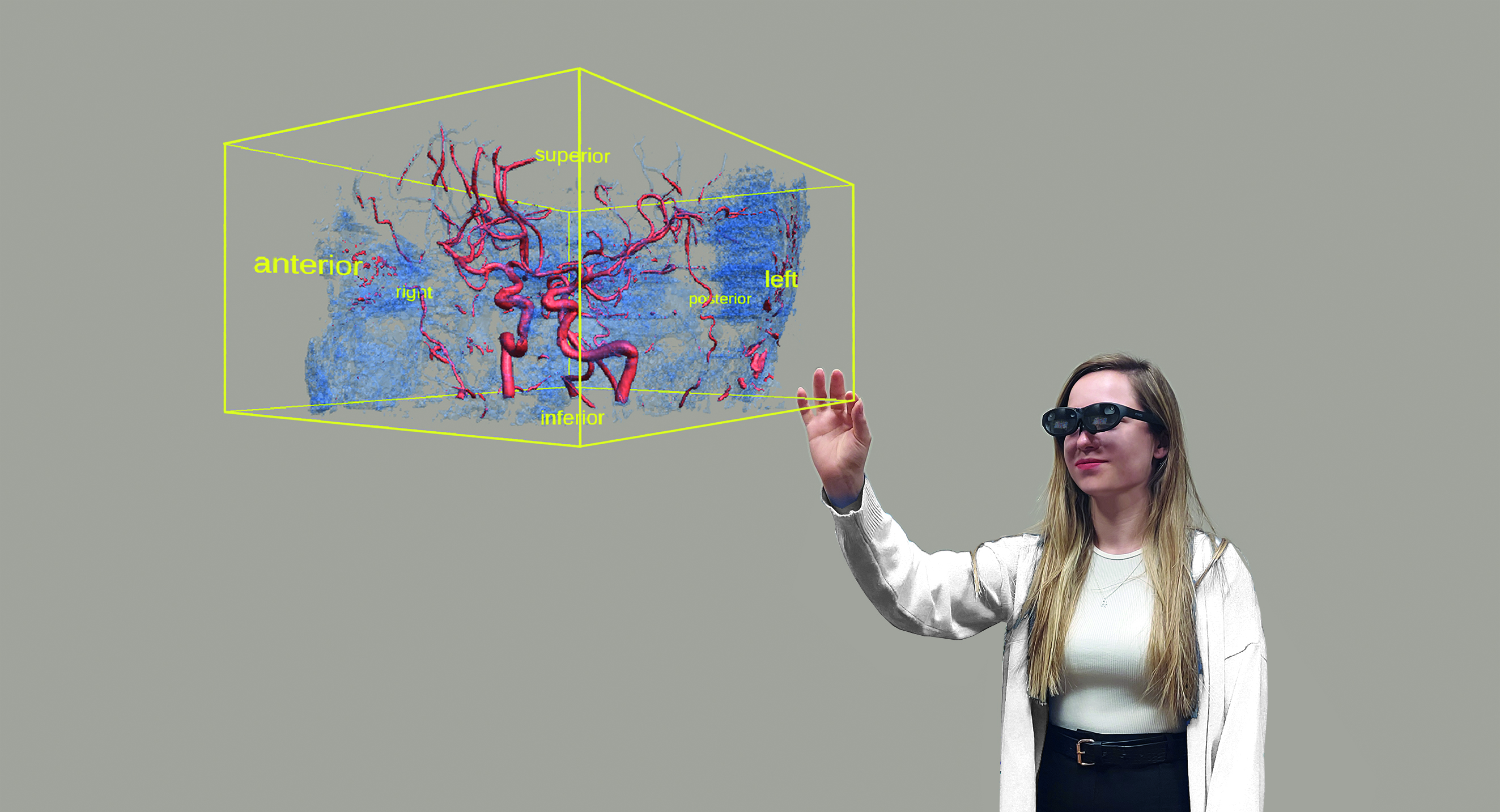
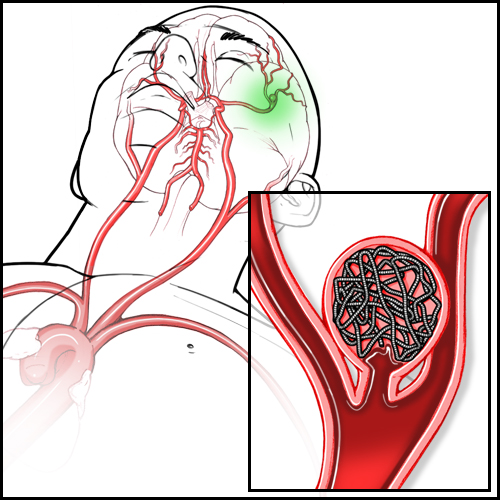
NEVSİM : Neuro-Endovascular Training Simulator
It is a completely virtual training simulator isolated from the world with VR glasses. In this use, the person who will receive the training wears glasses and sees the operation room (angio suite) in a completely virtual environment, and performs the interventional procedure with the help of a hand controller on a virtual model. In addition, as an additional ability not found in real life, progression in the vein is also displayed in 3D above the patient in the air.
It has contain 3 sub-simulators;
- Neuro-Endovascular VR Training Simulator
- Haptic Device Integrated Neuro-Endovascular AR Training Simulator
- Physical Vascular Path Model Integrated Neuro-Endovascular AR Training Simulator
In addition, these simulators address two different training stages as Guide Wire (microtel) and Catheter usage training and Neuro Endovascular pathology treatments training.
Automatic Detection System of Emergency Brain Diseases (TOTSIS)
Totsis is an artificial intelligence-based pre-diagnosis and early warning system. It is possible to detect anomalies such as cerebral hemorrhage and stroke from the CT images within a short period of 6-10 seconds after the CT image is taken, and prompt warning information is given to the relevant physician in line with this detection, and in case of a possible cerebral hemorrhage or stroke, the doctor can intervene immediately to the patient. makes it. Diseased areas and lesions on CT are segmented, labeled and controlled by physicians. In the labeling process, the region of interest is primarily marked with segmentation and masking, and the algorithm is provided to concentrate/focus on these regions.
With TOTSIS, it is a product with high added value that can be used especially in provinces, regions and countries where the number of specialist doctors is low.
